Research
Ph. D. Candidates
Arthur K. Barnes — Hybrid Microgrid
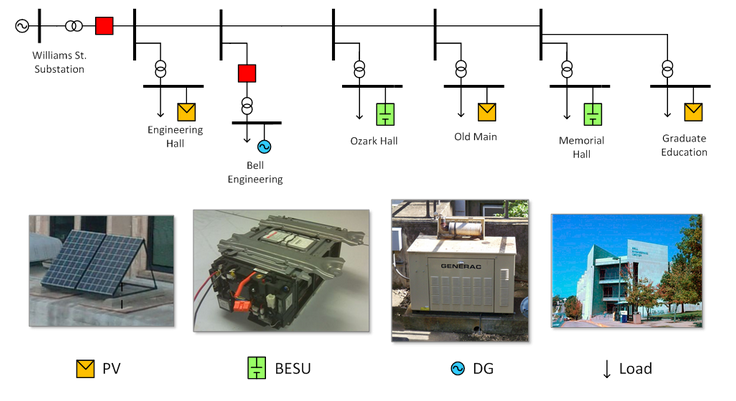
The second phase of this research project builds upon the results of the phase 1 project which considered a 480-V diesel-based microgrid. In phase 2, a medium-sized utility customer uses energy storage (ES) to reduce the cost of electricity and to improve voltage regulation. The customer uses a medium-voltage radial distribution system with a high penetration of photovoltaic (PV) generation and conservative voltage reduction for peak shaving in conjunction with varying cost of electricity. ES must be integrated appropriately into the distribution system to maximize provided benefits. The first step is to characterize the impact of distributed PV on the distribution system in terms of voltage regulation. The second step is to select appropriate battery chemistry and capacity, as well as the charge/discharge schedule. The last step determines the placement and power rating of each individual ES unit (ESU) in the distribution system. The placement and sizing must consider the ability of the ESU to coordinate with smart PV inverters – that is, include support for smart grid communication, VAr support, and curtailing of power output.
Andreas Escobar — Sizing Energy Storage for Wind Power Applications
Energy storage sizing to compensate wind intermittency. Integration of large-scale wind farms with the power grid using Multi-Terminal HVDC.
Masters Candidates
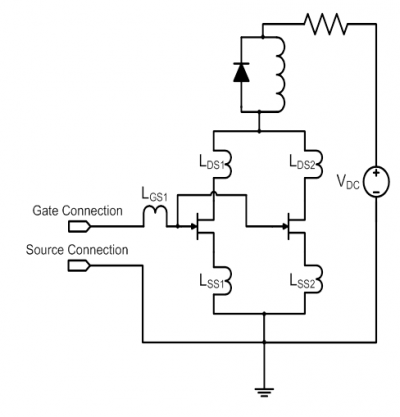
Corris Mallory Doss Stewart — Analysis and Implementation of Normally-off SiC JFETs
Develop and analyze gate driver and power layouts for Silicon-Carbide Junction Field-Effect Transistors that will be implemented in motor drive and distributed generation applications. Analysis to include areas of parasitics and energy consumption, among others.
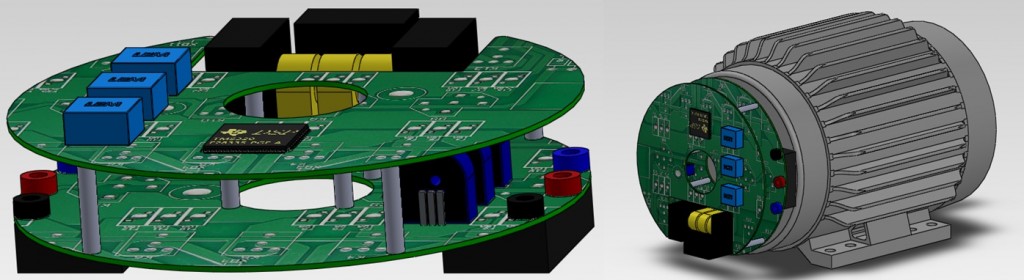
Jonathan Keith Hayes — Machine-Integrated Power Converters
The goal is to develop machine-integrated power converters taking advantage of new wide band gap semiconductor devices, like silicon carbide MOSFETs, and circuit topologies like indirect matrix converters that do not require electrolytic capacitors. The target is to obtain a power density in the range of fifty watts per cubic-centimeter.